 Urinary Incontinence is a common medical condition that affects over 40 million Americans, yet it often goes untreated or unrecognized. The reason for this trend is multifactorial, spanning from embarrassment to speak about this topic to dealing with more acute or morbid conditions that require focused attention.
Urinary Incontinence is a common medical condition that affects over 40 million Americans, yet it often goes untreated or unrecognized. The reason for this trend is multifactorial, spanning from embarrassment to speak about this topic to dealing with more acute or morbid conditions that require focused attention.
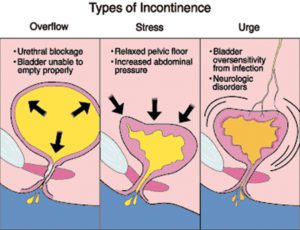
Nevertheless, it is a treatable condition that frequently affects the quality of life for patients. Incontinence is classified as stress, urge, mixed and overflow.
In this article we will address some particular issues about urge incontinence. Urinary urge incontinence (UUI) is defined as a sudden uncontrollable urge to urinate with or without frequent urination and associated leakage of urine. With urge incontinence, the bladder contracts and squeezes out urine involuntarily.
Accidental urination can be triggered by:
• sudden change in position or activity
• hearing or touching running water
• drinking a small amount of liquid
Patients with overactive bladder symptoms, such as urinary urgency, frequency and nocturia, may have associated incontinence over 60% of the time. Though more common in women than men overall, after the age of 70 the prevalence in both sexes is about equal.
There are two bladder abnormalities that are associated with UUI: neurogenic overactivity and detrusor overactivity (DO).
Neurogenic bladder occurs when there is interruption in the normal nerve conduction from the brain or spinal cord above the sacrum to the bladder, and results in loss of bladder sensation and motor control. Conditions associated with neurogenic bladder include the following:
• Alzheimer’s disease
• Multiple sclerosis
• Parkinson’s disease
• Intervertebral disk disease
• Cerebrovascular events
• Diabetes
• Traumatic brain or upper spinal cord injury
• Brain or spinal cord tumors
DO can occur due to multiple conditions, and many times as a sequel of others; frequently, it may be idiopathic. Dysfunctions of the detrusor muscle or nerve pathways are the culprits for the bladder over-activity. Conditions that can lead to DO include:
• Bladder polyps and tumors
• Urinary tract infections
• Bladder calculi
• Bladder outlet obstruction from BPH or stricture disease
Medications, such as diuretics, increase the urgency and frequency of urination in some people, especially the elderly and bedridden. Dosage modification may ameliorate the bothersome symptoms. Dietary habits may lead to significant voiding symptoms. Caffeine (e.g., in coffee, tea, chocolate), carbonated beverages, spicy foods and tomato-based foods can irritate the bladder and cause detrusor instability, resulting in urge incontinence.
The treatment and management of urge incontinence includes nonsurgical and surgical modalities. An important factor, however, is identifying the potentially morbid or life-threatening conditions that may lead to incontinence, such as bladder cancer, recurrent UTI or neurogenic disorders.
Advanced Urology Institute
855-298-CARE
Advancedurologyinstitute.com
 Central Florida Health and Wellness Magazine Health and Wellness Articles of the Villages
Central Florida Health and Wellness Magazine Health and Wellness Articles of the Villages



