 According to the Center for Disease Control, nearly 23% of all adults in the United States (more than 54 million people), suffer from arthritis. Arthritis, which can affect nearly any joint in the body, is an inflammation of one’s joints associated with the breakdown of cartilage. It causes painful symptoms such as swelling, stiffness, and decreased range of motion. While there are over 100 different types of arthritis, the two most common are rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Those who live with arthritis know its effects on everyday life, but what can happen should these forms of arthritis go untreated?
According to the Center for Disease Control, nearly 23% of all adults in the United States (more than 54 million people), suffer from arthritis. Arthritis, which can affect nearly any joint in the body, is an inflammation of one’s joints associated with the breakdown of cartilage. It causes painful symptoms such as swelling, stiffness, and decreased range of motion. While there are over 100 different types of arthritis, the two most common are rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Those who live with arthritis know its effects on everyday life, but what can happen should these forms of arthritis go untreated?
Osteoarthritis
Sometimes called degenerative joint disease or degenerative arthritis, osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common chronic condition of the joints, affecting approximately 27 million Americans. OA can affect any joint, but it occurs most often in knees, hips, lower back and neck, small joints of the fingers and the bases of the thumb and big toe.
In OA, the cartilage breaks down, causing pain, swelling and problems moving the joint. As OA worsens over time, bones may break down and develop growths called spurs. Bits of bone or cartilage may chip off and float around in the joint. In the body, an inflammatory process occurs and cytokines (proteins) and enzymes develop that further damage the cartilage. In the final stages of OA, the cartilage wears away and bone rubs against bone leading to joint damage and more pain.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system, which normally protects itself by attacking foreign substances like bacteria and viruses, mistakenly attacks the joints. This creates inflammation that causes the tissue that lines the inside of joints (the synovium) to thicken, resulting in swelling and pain in and around the joints. The synovium makes a fluid that lubricates joints and helps them move smoothly.
If inflammation goes unchecked, it can damage cartilage, the elastic tissue that covers the ends of bones in a joint, as well as the bones themselves. Over time, there is loss of cartilage, and the joint spacing between bones can become smaller. Joints can become loose, unstable, painful, and lose their mobility. Joint deformity also can occur.
What are my
treatment options?
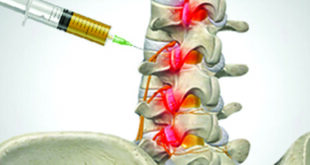
Two of the most common treatment options traditionally have been Cortisone shots or joint replacement surgery. Cortisone shots are typically given to mask the pain of arthritis and, may do more long-term harm to the joint than good. Side effects
include thinning of the soft tissue (cartilage) and skin around the injection site, and thinning of nearby bone. It’s for this reason, doctors will typically limit the number of cortisone shots into a given joint. The risks of joint replacement surgery are even more obvious. It carries all the risks of any invasive surgery: extreme pain, swelling, blood clots, potential nerve damage and infection to name a few. Add that to the known dangers and longterm negative effects of anesthesia and it is no wonder afflicted patients continue to look towards a different alternative: stem cell therapy.
Stem cell therapy doesn’t aim to mask the pain, but heals the very problem causing the pain in the first place. Unlike these traditional treatments, stem cell therapy is the only one which may actually help your body to regrow your natural cartilage.
For more information on how stem cell therapy may benefit you, please visit brandonstemcellclinic.com.
Brandon Stem Cell Clinic
1602 Oakfield Drive,
Suite 101
Brandon, FL 33511
 Central Florida Health and Wellness Magazine Health and Wellness Articles of the Villages
Central Florida Health and Wellness Magazine Health and Wellness Articles of the Villages